What is a risk reversal option strategy?
A risk reversal option strategy is a hedging strategy that involves the use of put and call options to protect a long or short position against unfavourable price movements in the underlying asset. When used for hedging, this strategy protects against potential losses by allowing investors to limit their exposure to market risk.
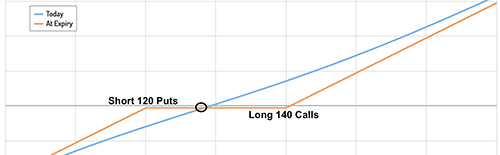
Risk Reversal Option Strategy
There are two basic variations of a risk reversal strategy used for hedging, as explained. The first variation involves selling an out-of-the-money put option and using the proceeds to buy an out-of-the-money call option. This strategy is commonly known as a bullish risk reversal strategy as it offers upside potential while protecting against downside risk. The second variation involves selling an out-of-the-money call option and using the proceeds to buy an out-of-the-money put option. This strategy is commonly known as a bearish risk reversal strategy as it offers downside protection while limiting upside potential.
A risk reversal option strategy is typically used by experienced traders such as institutional investors, as retail traders are generally unaware of its capabilities [3]. This strategy is particularly useful for investors who are holding a long or short position in an asset and want to protect their investment against price fluctuations. It is important to note that while a risk reversal strategy can limit the potential losses, it also limits the potential gains.
In summary, a risk reversal option strategy is a hedging strategy that involves the use of put and call options to protect a long or short position against unfavorable price movements in the underlying asset. There are two basic variations of a risk reversal strategy used for hedging, which are commonly known as bullish and bearish risk reversal strategies. This strategy is typically used by experienced traders and can be useful for investors who want to protect their investment against price fluctuations while limiting potential gains.
Is a Risk Reversal Option Strategy profitable?
The profitability of a risk reversal option strategy depends on market conditions and the specific implementation of the strategy.
A bullish risk reversal strategy, which involves selling an out-of-the-money put option and using the proceeds to buy an out-of-the-money call option, is profitable if the stock rises appreciably, and is unprofitable if it declines sharply. Conversely, a bearish risk reversal strategy, which involves selling an out-of-the-money call option and using the proceeds to buy an out-of-the-money put option, is profitable if the stock declines appreciably, and is unprofitable if it rises sharply.
In general, a risk reversal strategy is a hedging strategy that is designed to protect a trader’s long or short position by using put and call options. This strategy is particularly useful for investors who are holding a long or short position in an asset and want to protect their investment against price fluctuations. A risk reversal strategy can limit potential losses, but it also limits potential gains.
Moreover, a risk reversal strategy can also be used as a low-cost way to double down on a directional position or to manage some of the risks of a directional position.
In summary, the profitability of a risk reversal option strategy depends on market conditions and the specific implementation of the strategy. A bullish risk reversal strategy is profitable if the stock rises appreciably, while a bearish risk reversal strategy is profitable if the stock declines appreciably. However, a risk reversal strategy is primarily used as a hedging strategy to protect against price fluctuations and can limit potential losses while also limiting potential gains.
How to trade a Risk Reversal Option Strategy
An option risk reversal strategy is a hedging strategy that involves the simultaneous selling (or writing) of an out-of-the-money call or put option while simultaneously buying the opposite option. The purpose of this strategy is to protect against unfavorable price movements in the underlying asset by limiting potential losses and potentially increasing gains.
To implement this strategy, the trader must sell an out-of-the-money put option and simultaneously buy an out-of-the-money call option with the same expiration date. The premium received from selling the put can then be used towards buying the call. If the cost of buying the call is higher than the premium received for selling the put, the trader will have a net debit. Conversely, if the trader sells a call and buys a put, they will generate a net credit.
It is important to note that commissions must also be considered when trading a risk reversal strategy, as they can affect the overall balance of the trade. Moreover, a risk reversal strategy can have different meanings in different contexts. In commodities trading, a risk reversal strategy involves selling a call and buying a put option to protect against unfavourable, downward price movements in the underlying asset. In foreign exchange trading (forex), a risk reversal strategy refers to the volatility of out-of-the-money call or put options, where a positive risk reversal means that the volatility of call options is higher than that of the corresponding put options, and a negative risk reversal means the opposite.
In summary, a risk reversal strategy involves selling an out-of-the-money put option and simultaneously buying an out-of-the-money call option to limit potential losses and potentially increase gains. The trader can have a net debit or net credit depending on the cost of the call and the premium received from selling the put. Commissions must also be considered when trading this strategy. However, it is important to note that the definition of risk reversal can vary depending on the context in which it is used.
